
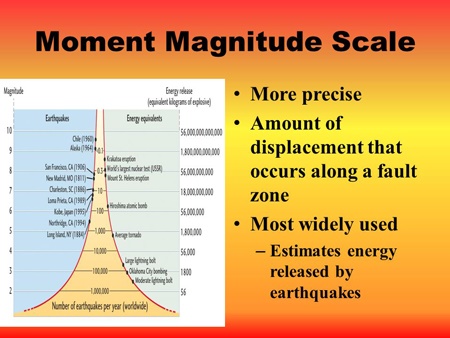
The largest earthquake ever recorded was in Chile in 1960, which measured 9.5 on the Richter scale. The moment magnitude scale is a calculation of the size of the surface along the fault that ruptured during the quake. Earthquakes measuring upwards of 7 are less frequent but very powerful, and can cause a lot of destruction. Earthquakes measuring 1-2 on the scale happen regularly, and they are so small that people cannot feel them. News media often report Richter magnitudes right after an earthquake occurs even though. It is logarithmic which means, for example, that an earthquake measuring magnitude 5 is ten times more powerful than an earthquake measuring 4. The moment magnitude (M W), which is measured using seismic arrays and generates values comparable to the Richter Scale, is more accurate for measuring earthquakes across the Earth, including large earthquakes, although they require more time to calculate. A Richter scale is normally numbered 1-10, though there is no upper limit. It should be noted that the geometry of the fault is considered by the moment magnitude scale. The moment magnitude scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on the seismic movement. It is measured using a machine called a seismometer which produces a seismograph. The statement that describes the moment magnitude scale is that it collects data using a seismograph. The Richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake (how powerful it is). A Willmore seismometer measures earthquakesĮarthquakes, until recently, have been measured on the Richter scale.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
